4 Essential Considerations for Implementing Server Side Tagging Successfully
Table of Contents
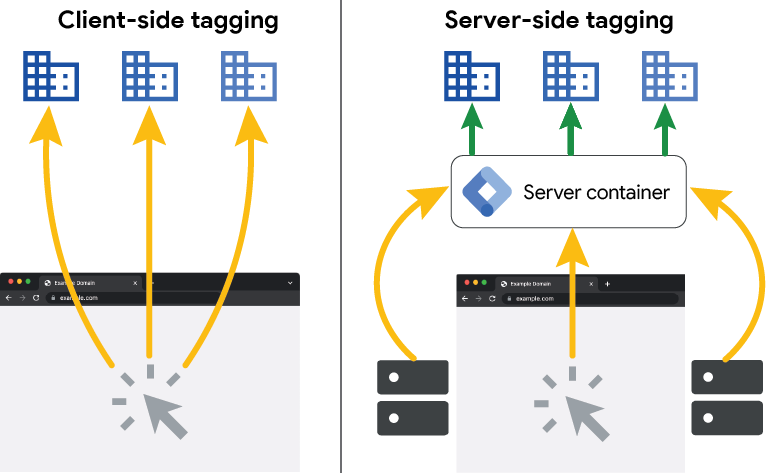
ToggleServer side tagging is a new and improved way to keep track of how users interact with a website. Unlike the old way, where many pieces of code, or tags, were put directly on the website (slowing it down).
Server side tagging does this work on a separate server managed by your company. This means websites can load faster and work better, improving the experience for users.
This new method is not just faster but also more secure, helping companies handle user data more responsibly and navigate through privacy laws more easily.
It also avoids problems with ad blockers, allowing uninterrupted collection and analysis of important data.
However, it’s not all upside. Implementing server side tagging can be more complex and might come with additional costs.
It requires careful planning and perhaps a new skill set or external expertise. When putting server side tagging into practice, keep the following in mind.
Vendor Template limitation in Server side Tagging
One current limitation in server side tagging is the limited number of vendors’ template tags. Even though the situation is expected to improve, some desired tags for specific vendors are not yet supported.
For marketers and analysts, the limited availability of vendors’ template tags in server side tagging can have several implications:
- Reduced Flexibility: Without the necessary vendor templates, marketers might be unable to deploy specific tracking or advertising functionalities that are integral to their campaigns.
- Increased Reliance on Custom Tags: In the absence of out-of-the-box tags, there may be a need to create custom tags, which can be time-consuming and require specific technical expertise.
- Delayed Decision-making: For analysts, missing templates can hinder the acquisition of valuable data. Without the proper tags, they might not get the insights they need on time, leading to delays in decision-making or strategy adjustments.
- Inconsistent Data Collection: Some vendor-specific tags might offer unique data collection methods or parameters. Without them, there could be inconsistencies in the data gathered, affecting the accuracy of analyses.
- Increased Costs: Relying on custom solutions or third-party integrations to compensate for the missing vendor templates could result in additional costs.
- Operational Delays: The process of waiting for a vendor template to be supported or creating a workaround might delay the rollout of marketing initiatives, causing potential missed opportunities.
Challenges in the Validation Process of Server side Tagging
The server side tagging validation process is critical for ensuring data accuracy and system reliability. It still presents its own set of challenges:
- Data Consistency Issues: Validating data between the server and client side can sometimes highlight inconsistencies, making it challenging to pinpoint the source of the discrepancy.
- Complex Error Handling: Given the added layer of server processing, identifying and rectifying errors can become more intricate, necessitating deeper technical proficiency.
- Technical Demands: The server-side validation process is inherently more technical, often requiring specialized knowledge and tools for effective execution.
- Time-Consuming Troubleshooting: When discrepancies arise, tracing them back through the server-side processing chain can be time-intensive, slowing down the overall analytics workflow.
Data Discrepancies in Server side Tagging
Shifting from client side to server side tagging introduces new challenges, with data discrepancies at the forefront.
It is critical to ensure data consistency between the two sides for accurate analytics and reporting. Here are some examples of data discrepancies:
- Mismatched Metrics: The difference in how data is processed and collected server-side versus client-side can lead to mismatched or conflicting metrics. This can be perplexing for analysts trying to interpret the results.
- Incomplete Data Capture: If server side tagging isn’t set up to mirror the exact data points collected client-side, it can lead to gaps in the data, which in turn affects the comprehensiveness of the reports.
- Inaccurate Session Tracking: Vital client-side information like client ID and IP address must be correctly passed on to the server side. If not, it might misrepresent user interactions, skewing session-based metrics.
- Potential for “(no set)” Values: Missing data can result in “(no set)” appearing in reports, which indicates gaps in data collection or transmission.
Data Latency in Server side Tagging
Implementing server side tagging may raise concerns about data latency. Adding a server to the data collection chain can result in increased latency
- Added Processing Time: The involvement of an additional server necessitates extra time for the data to be received, processed, and forwarded to its final destination, potentially causing substantial delays.
- Optimization Issues: A server that is not optimized aptly can lead to sluggish data processing and transmission, impacting the timeliness of data availability.
- Network Complications: Any network-related issues can further augment the latency, making real-time or near-real-time data access challenging.
Conclusion
In conclusion, server side tagging is becoming increasingly important for online data analysis.
However, the true strength of this tool doesn’t just lie in its core functions; its effectiveness is determined by how well it is implemented and how well it aligns with the specific needs of a business.
As a result, businesses should proceed with caution when implementing server side tagging.
While it is a valuable tool for data capture and management, its effectiveness depends on the quality of its implementation.
Happy implementing